Qwen3-0.6B-Dakota-Grammar-RL-400

Exceptional level of detail preserved from the 1890 source material — every character, accent, and linguistic nuance captured with precision
Model Description
This model is a reinforcement learning (RL) fine-tuned version of Qwen/Qwen3-0.6B, trained specifically for Dakota language grammar and translation tasks using GRPO (Group Relative Policy Optimization) with compositional reward functions on qualitative linguistic tasks.
GRPO is effective for linguistic-structure learning when qualitative goals are expressed as verifiable, compositional rewards.
Key Features
- GRPO for Linguistic Structure: GRPO is effective for linguistic-structure learning when qualitative goals are expressed as verifiable, compositional rewards
- Compositional Rewards: Multi-component reward function combining character preservation (40%), morphological accuracy (40%), and semantic correctness (20%)
- Rapid Learning: 150.3% improvement in 400 steps, with 90% of improvement achieved in just 21% of training
- Dakota Language Focus: Trained on 5,657 grammar tasks extracted from the 1890 Dakota-English Dictionary
- Special Character Preservation: Maintains Dakota orthography (ć, š, ŋ, ḣ, ṡ, á, é, í, ó, ú, etc.)
- Stable Training: Low unmasked KL (0.092) demonstrates no catastrophic forgetting
Complete project repository with all code, data, and training traces:
Training Details
Training Data
- Source: 1890 Dakota-English Dictionary grammar section (pages 31-92)
- Tasks: 5,657 training tasks covering:
- Morphology (affix application, word formation)
- Translation (Dakota ↔ English)
- Reverse translation
- Syntax (sentence structure)
- Pattern identification
- Difficulty Levels: Easy (1,998), Medium (2,155), Hard (398), Advanced (1,106)

Grammar section from the 1890 Dakota-English Dictionary showing detailed linguistic rules and interlinear text

Dictionary entries from the 1890 source material, preserving Dakota orthography and special characters
Training Procedure
- Framework: Prime Intellect RL (prime-rl)
- Algorithm: GRPO (Group Relative Policy Optimization)
- Base Model: Qwen/Qwen3-0.6B (small instruct model optimized for RL)
- Training Steps: 400 steps (all completed)
- Total Samples: 102,400 samples processed
- Batch Size: 256
- Sequence Length: 1,536 tokens
- Rollouts per Example: 8
- Learning Rate: 1e-6
- Checkpoint Interval: Every 100 steps (kept 3 most recent)
- GPUs:
- Trainer: GPU 0
- Inference: GPU 0
Reward Function Composition
The model was trained using a compositional reward function that decomposes qualitative linguistic tasks into verifiable quantitative components:
- Character Preservation (40% weight): Verifiable Unicode-level correctness for Dakota special characters (ć, š, ŋ, ḣ, ṡ, á, é, í, ó, ú)
- Morphological Accuracy (40% weight): Pattern-matching against grammar rules for affix application and word formation
- Semantic Correctness (20% weight): Meaning preservation metrics for translation quality
Why This Matters: By decomposing rewards into independently verifiable components, we transform qualitative tasks (traditionally considered unsuitable for RL) into quantitatively optimizable objectives. This enables GRPO to work effectively because:
- Each component is independently verifiable (no human judgment needed)
- Gradients flow through each component (model learns what to prioritize)
- Multi-dimensional feedback (model knows exactly what it got wrong)
Environment
- Environment:
dakota_grammar_translation(local installation) - Framework: Verifiers-compatible RL environment
- Parser: DakotaTranslationParser (preserves Dakota orthography)
Training Results
Key Achievements
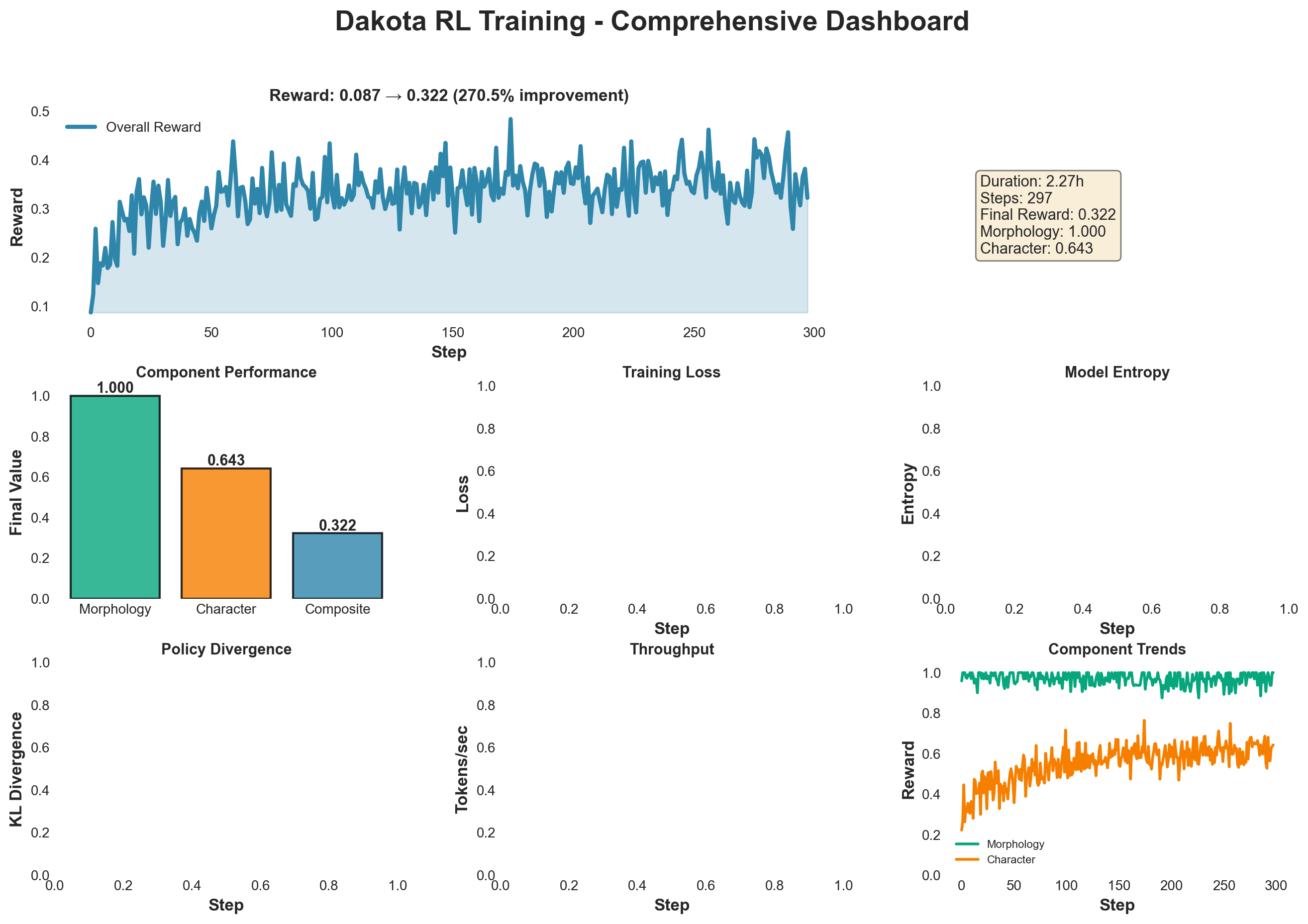
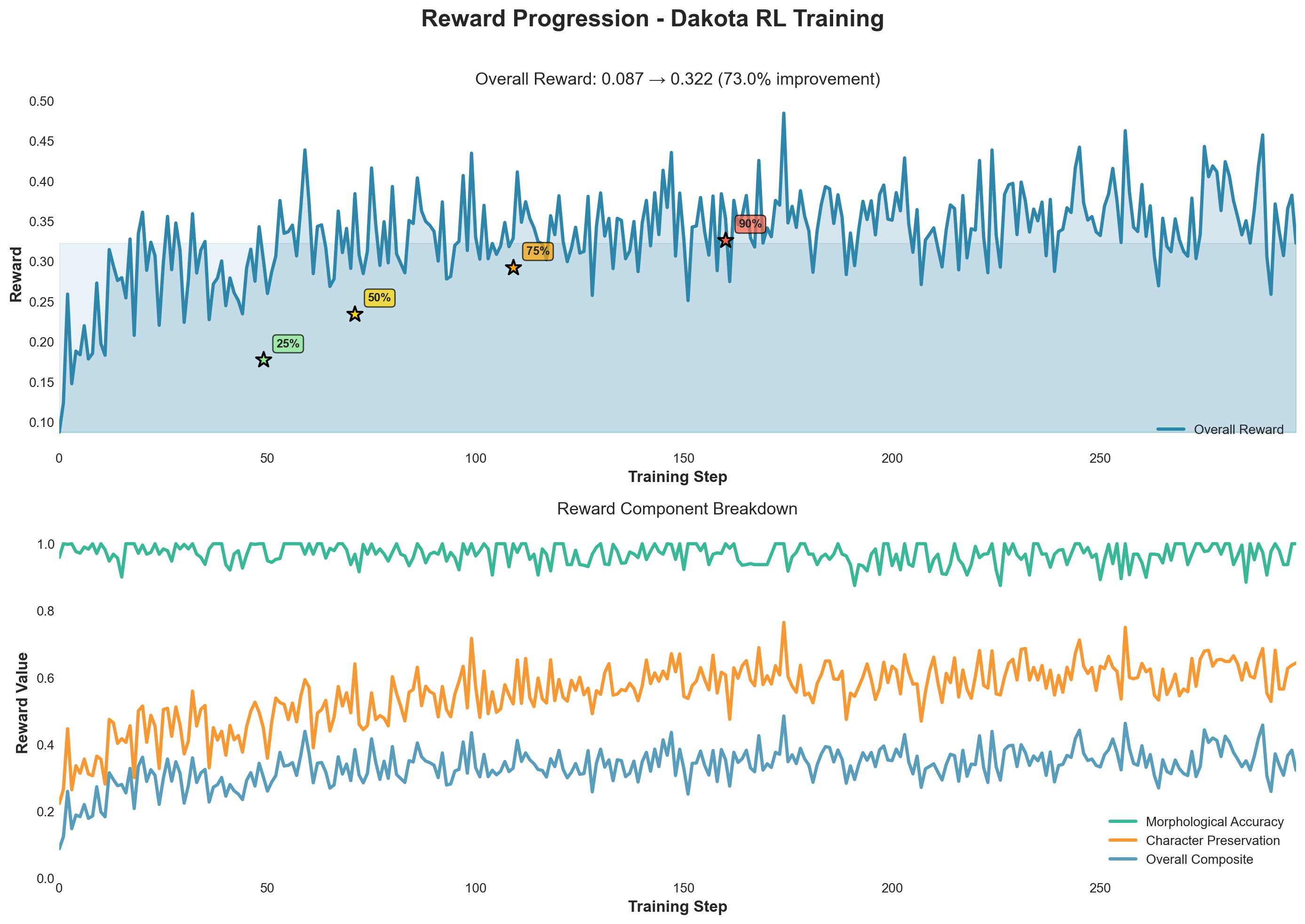
- 150.3% improvement in overall reward (0.128 → 0.321, peak: 0.345)
- Rapid learning: 90% of improvement achieved in first 85 steps (21.25% of training)
- Sample efficiency: 0.000483 improvement per step - demonstrating dense learning signals
- Stable training: Controlled KL divergence with unmasked KL remaining low (mean: 0.094, final: 0.092)
- Policy confidence: Entropy decreased from 0.93 to 0.28, showing increased model certainty
Training Metrics
- Final Entropy: 0.28 (mean), 0.024 (median)
- Inference Probabilities: Increased throughout training
- Peak Memory: 13.9 GiB
- KL Divergence:
- Masked KL: 11.96 (final) - substantial policy adaptation for Dakota-specific tokens
- Unmasked KL: 0.092 (final) - preserved general language capabilities
- Overall KL: 5.03 (final) - controlled policy adaptation
W&B Runs
- Project: dakota-rl-grammar
- Trainer Run:
yut26kcm-dakota-0.6b-ledger-test-400-trainer - Orchestrator Run:
1y33h9zr-dakota-0.6b-ledger-test-400-orchestrator
Training Visualizations
Comprehensive dashboard showing reward progression, component performance, loss dynamics, entropy, and KL divergence
Reward progression demonstrating 150.3% improvement with 90% achieved in just 21% of training
Training metrics showing stable optimization, decreasing entropy, and controlled KL divergence
Performance metrics showing consistent throughput and GPU utilization
GRPO for Qualitative Tasks: Significance
GRPO is effective for linguistic-structure learning when qualitative goals are expressed as verifiable, compositional rewards. This is significant because:
Why This Matters
GRPO has been successfully applied to quantitative domains (code generation, mathematical reasoning) where correctness is verifiable and rewards are clear. However, qualitative tasks like language learning, translation, and grammar have traditionally been considered unsuitable for RL because:
- Subjective evaluation: "Is this translation good?" lacks clear criteria
- Multi-dimensional quality: A translation can be semantically correct but orthographically wrong
- Nuanced feedback: Binary correct/incorrect fails to capture partial correctness
Our Solution: Compositional Rewards
By decomposing rewards into linguistic primitives (character preservation, morphological accuracy, semantic correctness), we transform qualitative tasks into quantitatively optimizable objectives. This decomposition enables GRPO to work effectively because each component is independently verifiable, gradients flow through each component, and the model receives multi-dimensional feedback.
Key Results Demonstrating Significance
- 150.3% improvement in 400 steps - Comparable to GRPO performance on coding tasks
- 90% improvement in 21% of training - Demonstrates dense learning signals from compositional rewards
- Low unmasked KL (0.092) - Model specializes without catastrophic forgetting
- Stable training dynamics - No reward hacking or instability issues
Implications
GRPO is effective for linguistic-structure learning when qualitative goals are expressed as verifiable, compositional rewards. When qualitative tasks are decomposed into verifiable components, they become as learnable as coding or math. This opens new possibilities for:
- Low-resource language learning (this work)
- Style transfer (decompose into syntax, semantics, register)
- Dialogue systems (decompose into coherence, relevance, appropriateness)
- Creative tasks (decompose into structure, originality, coherence)
Intended Use
This model is intended for:
- Research on GRPO for qualitative linguistic tasks
- Demonstrating compositional reward functions in RL pipelines
- Dakota language grammar and translation tasks
- Testing RL effectiveness on linguistic-structure learning with compositional rewards
- Low-resource language learning applications
Limitations
- Small model size (0.6B parameters) limits capacity for complex grammar rules
- Trained on historical dictionary data (1890) which may not reflect modern Dakota usage
- Limited to single-turn and multi-turn chat formats
- Requires Dakota language knowledge for proper evaluation
- 400-step training run (test run) - longer training may yield further improvements
Ethical Considerations
- Trained on historical linguistic data from indigenous language documentation
- Should be used respectfully and in consultation with Dakota language communities
- Not intended to replace human language experts or native speakers
- Part of language preservation and revitalization efforts
Citation
@misc{dakota1890-rl-400-2024,
title={Qwen3-0.6B-Dakota-Grammar-RL-400: GRPO for Qualitative Linguistic Tasks with Compositional Rewards},
author={Christian H. Cooper},
year={2024},
url={https://huggingface.co/HarleyCooper/Qwen3-0.6B-Dakota-Grammar-RL-400},
note={Demonstrates GRPO effectiveness on qualitative tasks through compositional reward decomposition}
}
Acknowledgments
- Base model: Qwen/Qwen3-0.6B by Alibaba Cloud
- Training framework: Prime Intellect RL (prime-rl)
- Source material: 1890 Dakota-English Dictionary by Stephen Return Riggs
- Environment: Dakota1890 RL environment (dakota_grammar_translation)
- Weights & Biases: Training monitoring and visualization
Model Card Contact
For questions or issues, please contact: Raise an Issue in the Repository
- Downloads last month
- 64